ROOTS
Secondary Growth
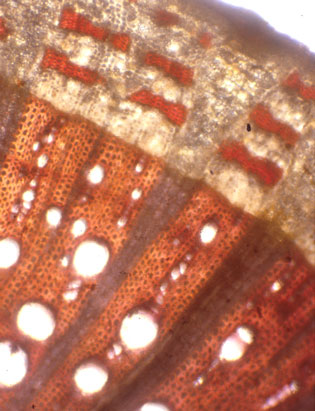
Secondary growth in roots begins with the formation of the vascular cambium. This concentric, undifferentiated cell layer originates from the pericycle and from the procambium, which is located between the primary xylem and primary phloem tissues. The vascular cambium continues to divide and differentiate to produce secondary vascular tissue toward the center of the root and secondary phloem tissue toward the outside of the root. The pericycle also gives rise to the cork cambium, which produces the periderm to the outside of the root.
In the image at left, secondary vascular tissue is lignified and stains red. The short bands of red-stained tissue in the secondary phloem tissue are phloic fibers.