
 THE SHOOT APICAL MERISTEM
(WONDERS OF THE SAM)
THE SHOOT APICAL MERISTEM
(WONDERS OF THE SAM)


-
what
is a meristem?
-
functions
of the meristem
-
structure
of the meristem
-
cell
activity within the meristem
WHAT IS A MERISTEM?
In
the early stages of development of the plant embryo all the cells undergo
division, but with further growth and development cell division and multiplication
become restricted to special parts of the plant which exhibit very little
differentiation and in which tissues remain embryonic in character and
the cells retain the ability to divide. These embryonic tissues in
the mature plant body are called meristems.
Meristematic
cells are usually thin-walled, more isodiametric in shape than the cells
of mature tissues, and relatively richer in protoplasm.
FUNCTIONS OF THE MERISTEM
All plants have meristems; these
are the most important sites of growth and the originating sites of cell
differentiation. Looking at a meristem under the microscope you can see
an amazing variety of things happening. Many cells are dividing, these
will look small and crunched together. Others are beginning their differentiation
process and you can see the formation of secondary walls. Differentiation
is the process a cell undergoes to become specialized for a certain funciton.
STRUCTURE OF THE MERISTEM
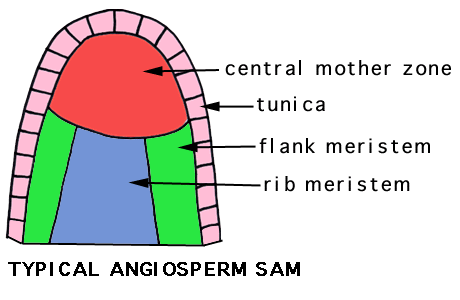
CELL ACTIVITY WITHIN THE MERISTEM
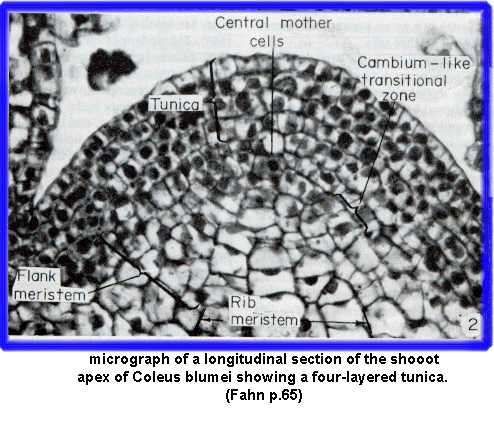
 Introduction | Flowers&Fruit
| Roots | Stems
| Leaves
Introduction | Flowers&Fruit
| Roots | Stems
| Leaves
© Thomas L. Rost 1997
Section of Plant Biology
Division of Biological Sciences
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, DAVIS






