|
|
|
|
|
Cortex and Pith
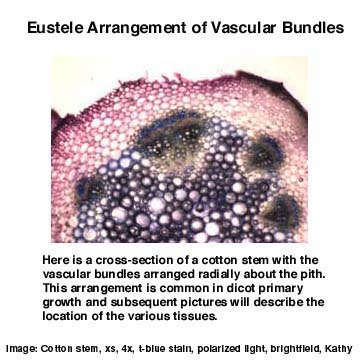
This cross-section has a good view of a stem showing very clearly the cortex in relation to the epidermis and the vascular bundles and pith. The cortex is mainly thin-walled parenchyma cells with some chlorenchyma immediately subtending the epidermal tissue.
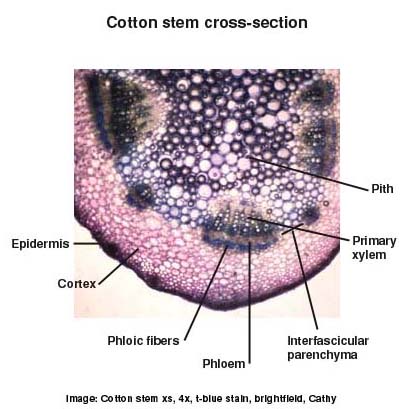
To read about primary growth in the vascular tissue system...
|
|
Introduction | Flowers&Fruit | Roots | Stems | Leaves Section of Plant Biology Division of Biological Sciences UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, DAVIS |